Session Description Protocol
This is used to:
- specify things like the details of what transport connections are to be set up,
- exchange the set of candidate IP addresses on which they can be reached, to set up the peer-to-peer connection.
- specify the media formats they want to use.
- Is it just audio? Or is it audio and video?
- And which compression algorithms are to be used?
- And they want to specify the timing of the session, and the security parameters, and all the other parameters.
SDP Offer/Answer
Interactive sessions require negotiation
- An offer to communicate: lists codecs, options and addressing details, identity of caller
- The answer subsets codecs and options to those mutually acceptable, supplies addressing details, and confirms willingness to communicate
- ICE algorithm (→ Lecture 2) probes NAT bindings, establishes path
- Audio and video data flows
Format
It’s essentially a set of key-value pairs, where the keys are all single letters, and the values are more complex, one key-value pair per line, with the key and the value separated by equals signs.
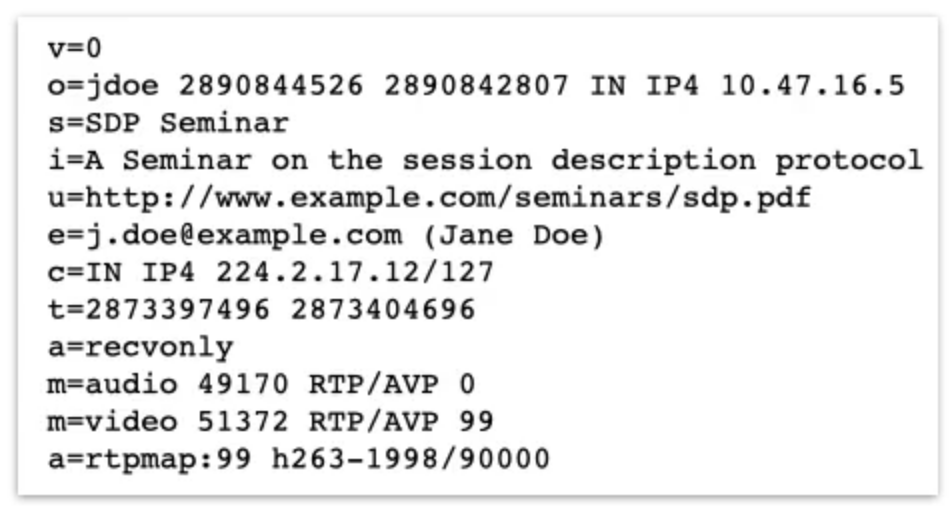 And, as we see in the example:
And, as we see in the example:
- it starts with a version number, v=0.
- There’s an originator line, and it was originated by Jane Doe, who had IP address 10.47.16.5.
- It’s a seminar about session description protocol.
- It’s got the email address of Jane Doe, who set up the call,
- it’s got their IP address, the times that session is active,
- it’s receive only, it’s broadcast so that the listener just receives the data,
- it’s sending using audio and video media,
- it specifies the ports and some details of the video compression scheme, and so on.