UDP is the simpler of the two Transport Layer protocols. It is a fundamentally connectionless, best effort, packet delivery method. It uses a 16 bit port number to identify services, but has no form of congestion control. it also exposes the raw IP service to applications.
Generally UDP is used for two case scenarios:
- Applications that prefer timeliness over reliability
- Voice-Over-IP (VoIP)
- Streaming Video
- Gaming
- New attempts at Transport Layer protocols:
- QUIC - UDP is a very simple protocol which allows for it to be built on top of
Any application using UDP must be able to:
- Handle packet loss
- Adapt to congestion of the Network Layer
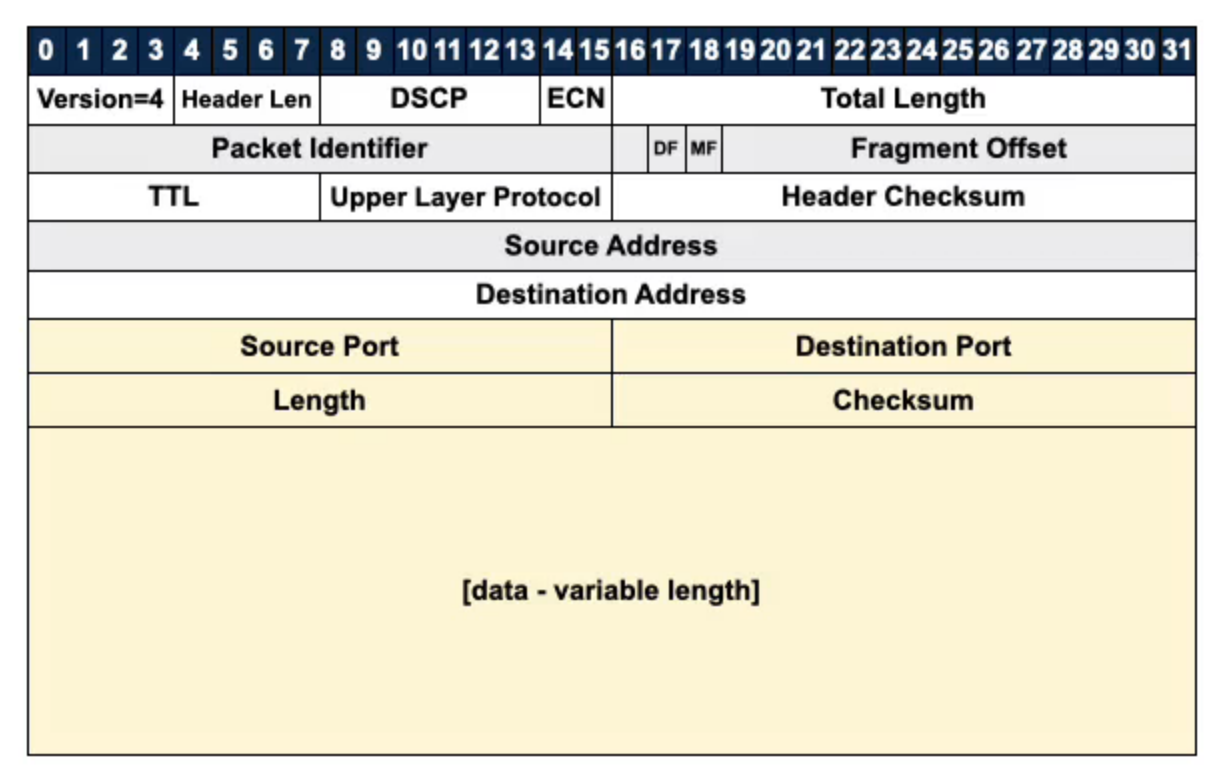
Adds Port Numbers and Check Sum to Internet Protocol UDP is immensely minimal and is the best platform for building other protocols on top of, such as:
- QUIC
- RTP
- DNS