The data link layer provides framing, addressing, Media Access Control • Structure the bitstream into meaningful frames of data • Detect and correct transmission errors • Identify devices • Arbitrate access to the channel
Framing & Addressing
This is the process of separating the bitstream into meaningful “frames” of data:
Ex: Ethernet
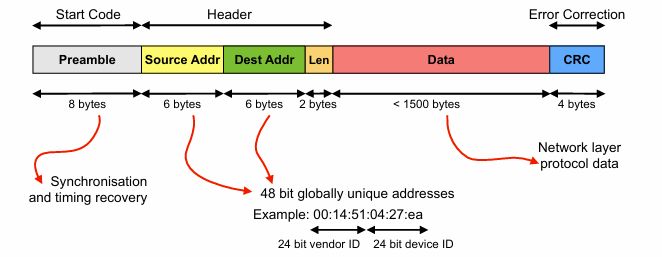
We can see that our Ethernet frame has:
- Preamble: Technically unimportant bits, which are used to synchronize frames, and understand timing of the system
- Source Address: Where the data is coming from, in the form of 48 bits, 24 bits of vendor ID. and 24 bits of device ID.
- Destination Address: Where the data is coming from, in the form of 48 bits, 24 bits of vendor ID. and 24 bits of device ID.
- Length: A verification, helps with calculations, length of the data, 2 bytes
- Data: This is the Network Layer protocol data.
- Error Correction - This handles things like Bit Errors