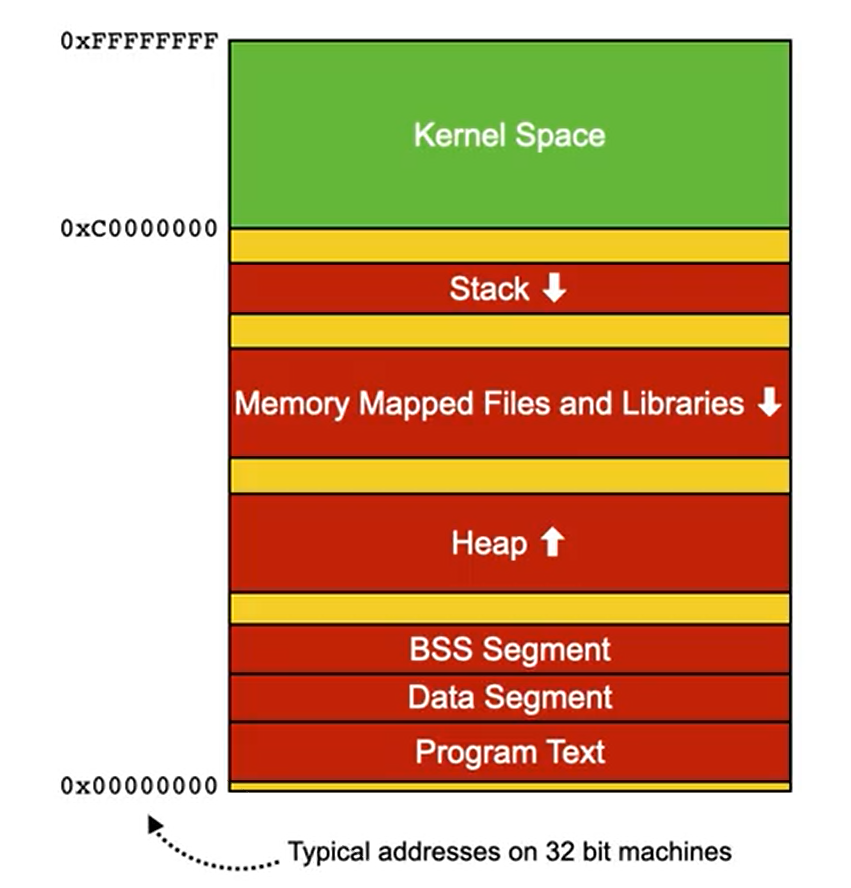
Memory Layout in Processes
- Process memory consists of several regions:
- Program text (machine code)
- Static data and global variables
- BSS segment (uninitialized globals)
- Heap (explicitly allocated memory)
- Memory mapped files
- Stack (function parameters, return addresses, local variables)
- Kernel space
Stack Memory Management
- Stack frames created/destroyed automatically with function calls
- Contains function parameters, return address, and local variables
- Buffer overflow attacks can overwrite return addresses
- Modern protections: stack randomization, non-executable memory
Automatic Memory Management Approaches
-
Reference Counting:
- Each object has a counter of references to it
- Counter increases when new reference created
- Counter decreases when reference removed
- When counter reaches zero, object is deallocated
- Advantages: predictable, intuitive, incremental
- Disadvantages: overhead, can’t handle cyclic references
-
Region-Based Memory Management (used in Rust Programming Language and discussed in Type Systems and Rust Programming Language):
- Lifetimes of objects tied to lexical scopes
- Compiler tracks object lifetimes and inserts cleanup code
- Box<T> type for heap allocation with automatic cleanup
- Enforced by ownership rules and borrowing
- Advantages: deterministic, no runtime overhead
- Disadvantages: more restrictive programming model
-
Garbage Collection (see dedicated note):
- Various algorithms: mark-sweep, mark-compact, copying
- Automatically reclaims memory that is no longer reachable
- Advantages: programmer convenience
- Disadvantages: performance overhead, unpredictability
Region-Based Memory Management Details
- Every value has a unique owner
- Compiler tracks lifetime of values
- When a value goes out of scope, it’s automatically deallocated
- Prevents use-after-free bugs and memory leaks
- Rust rules prevent returning references to local variables
- Rules also prevent accessing values after they’re freed
Resource Management Beyond Memory
- Ownership tracking can manage any resource (files, locks, etc.)
- Custom destructors (via
Droptrait) provide cleanup - State machines can use ownership to enforce transitions (see Type-Driven Development)